티스토리 뷰
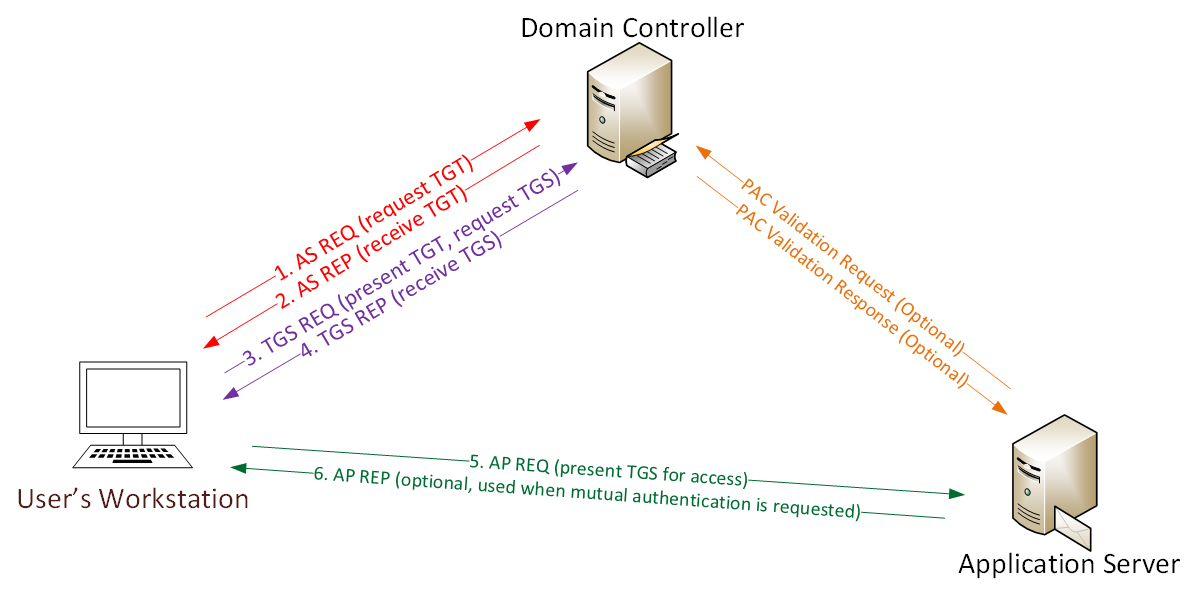
User logs on with username & password.
1a. Password converted to NTLM hash, a timestamp is encrypted with the hash and sent to the KDC as an authenticator in the authentication ticket (TGT) request (AS-REQ).
1b. The Domain Controller (KDC) checks user information (logon restrictions, group membership, etc) & creates Ticket-Granting Ticket (TGT).
2. The TGT is encrypted, signed, & delivered to the user (AS-REP). Only the Kerberos service (KRBTGT) in the domain can open and read TGT data.
3. The User presents the TGT to the DC when requesting a Ticket Granting Service (TGS) ticket (TGS-REQ). The DC opens the TGT & validates PAC checksum – If the DC can open the ticket & the checksum check out, TGT = valid. The data in the TGT is effectively copied to create the TGS ticket.
4. The TGS is encrypted using the target service accounts’ NTLM password hash and sent to the user (TGS-REP).
5.The user connects to the server hosting the service on the appropriate port & presents the TGS (AP-REQ). The service opens the TGS ticket using its NTLM password hash.
6. If mutual authentication is required by the client (think MS15-011: the Group Policy patch from February that added UNC hardening).
Unless PAC validation is required (rare), the service accepts all data in the TGS ticket with no communication to the DC.
'CyberSecurity' 카테고리의 다른 글
| vmware 에서 ubuntu 사용하다가 디스크 용량 늘리고 싶을때 (0) | 2020.06.17 |
|---|---|
| Simple and Basic but Critical (0) | 2018.12.07 |
| 이걸 왜 여지껏 몰랐지 pathping (0) | 2018.12.03 |
| 7 Cybersecurity Trends in 2018 (0) | 2018.08.08 |
| Facial Recognition (0) | 2018.05.29 |
